What is a fungus or fungal disease?
- Pathogens: Various types of parasitic fungi (pathogenic and opportunistic).
- Affected areas: skin, nails, hair, mucous membranes.
- Relapse: Very likely.
causes of fungal diseases
decrease in immunity
Insufficient hygiene when using public places
- If one goes to a swimming pool or public bath, one always needs to bring a personal towel and flip-flops with them.
- You should do the same when you go to the gym.
- It is recommended to wear only socks to the store to try on shoes.
- It is necessary to ensure that the salon professionals do not forget to sterilize the instruments.
- Do not use other people's toiletries.
- Tight shoes or synthetic underwear are not recommended.
- If the skin is damaged, you should not forget about antiseptics, since infection occurs through damaged areas.
chronic disease
characteristics of characters
Types of fungi
- Calatomycosis - when microorganisms are present only in the stratum corneum of the skin;
- Dermatophytosis - if the fungal infection successfully penetrates the epidermis, hair follicles and dermis;
- Candidiasis - Mucosal damage.
- Yeast is often part of the microbiome.
- Molds are pathogenic.
- Dodmiphorae are pathogenic.
How to Recognize Fungal Disease - Symptoms
- Changes in skin color - redness or loss of color;
- Have areas of persistent peeling or leakage;
- itching;
- Crust.
- Symptoms of fungus are usually dandruff;
- Fragility and hair loss.
- Lesions appear in the upper eyelid folds.
- crack;
- combustion;
- bubble;
- More common is an unpleasant odor;
- Rough skin;
- Thickening of the skin;
- Ulcers (if there is also a bacterial infection).
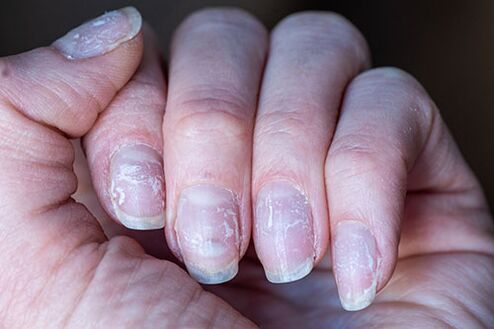
- There are small white spots on the plate;
- Affected nail has white streaks;
- Color changes to black, yellow, brown;
- The structure changes (becomes stratified);
- Thickening or thinning of nails;
- The nail plate moves away from the bed;
- Inflamed nailfold;
- Changes in nail shape or relief.
Medications to Treat Fungus
- Drugs used to treat spore-destroying fungi - fungicides;
- Those drugs that do not inhibit the development of a fungal infection and prevent its growth, but do not eliminate it, are fungistats.
- Dosage of active substance;
- Spectrum of action of active substances.
Post form
- ointment;
- cream;
- spray;
- solution;
- Antifungal varnish (for nail lesions).